2 min read
Understanding Far-UVC and Equivalent Air Changes: A Guide to Advanced Air Purification
 Cecilie Aaberg Meltofte
:
08 Jul, 2024
Cecilie Aaberg Meltofte
:
08 Jul, 2024
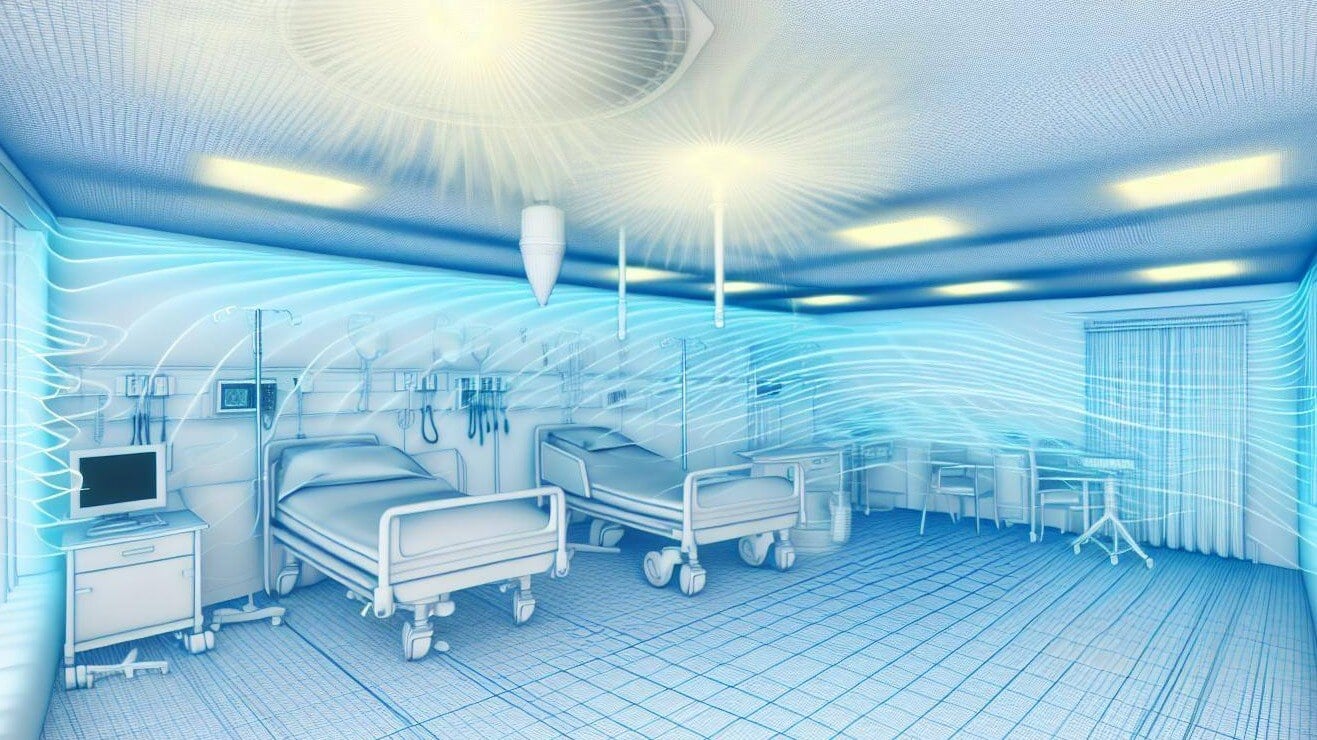

Published Nature in 2022, a scientific paper titled "Far-UVC (222 nm) efficiently inactivates an airborne pathogen in a room-sized chamber" was authored by prominent researchers within the Far-UVC community. The study found that Far-UVC technology can achieve 35 air changes per hour in less than 15 minutes for air disinfection. For comparison, a hospital operating room typically requires 20 air changes per hour.
The Equivalence of Air Changes per Hour
Air changes per hour (ACH) is a calculation of how many times the volume of air in a room is fully replaced in one hour, typically using ventilation systems. To compare how Far-UVC affects the number of ACH, a group of researchers built a mechanically ventilated room with a size of 32 m3 and installed Far-UVC lamps in the ceiling. Airborne Staphylococcus aureus bacteria were continuously introduced to the room at one end. By collecting samples before and after the Far-UVC lamps were turned on, they could calculate the equivalent air changes per hour (eACH) and compare the efficacy to ventilation alone.
Staphylococcus aureus is known for its ability to become multi-drug resistant (MRSA) and its implications in severe hospital acquired infections
Reach 35 equivalent air changes per hour in less than 15 minutes
The researchers investigated several settings of the Far-UVC lamps within regulatory limit values. They found that when the setting was in compliance with the lowest threshold limit value set by ICNIRP (23 mJ/cm2), they achieved a 92% reduction of airborne S. aureus compared to using baseline ventilation of three ACH alone. This corresponds to 35 equivalent air changes per hour (eACH), which is 11 times the baseline ventilation reached in less that 15 minutes.
When the lamps were configured to comply with the highest threshold limit values set by ACGIH (479 mJ/cm2), they reduced the load of S. aureus by 98.4%, corresponding to 184 eACH.
In short, the study demonstrates how Far-UVC can markedly improve air quality while staying in compliance with even the strictest regulatory limits.
Lower the Risk of Surgical Site Infections
The study highlights the potential of Far-UVC technology in sterile environments such as operating rooms, where it is crucial to maintain germ-free air to reduce the risk of surgical site infections (SSIs). While ventilation plays a role in air purification, increasing the air changes per hour solely through ventilation can be costly due to high energy consumption. Far-UVC, being safe for human exposure, can be installed to cover the entire operating room, continuously inactivating airborne pathogens during surgery.
Far-UVC is chemical-free, mercury-free, and energy-efficient, making it an effective and environmentally friendly solution for enhancing patient safety in operating rooms.
The Essence of Far-UVC Technology
Far-UVC technology is renowned for its potent ability to inactivate airborne pathogens, creating a cleaner and safer environment. Operating as a specific wavelength of 222 nm, Far-UVC light efficiently targets and eliminates viruses and bacteria, including disease-causing pathogens coronaviruses and influenza. Unlike conventional UVC light, Far-UVC is designed with human safety in mind, being harmless to human skin and eyes.
Using Far-UVC to Improve Indoor Air Quality
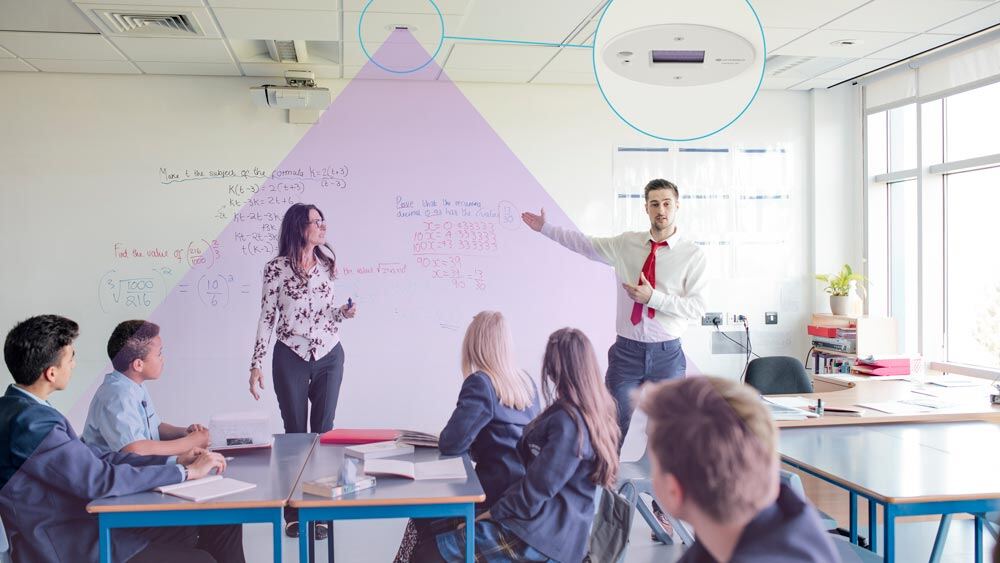
The use of Far-UVC technology to improve air quality is not limited to operating rooms; it can also be utilized in various settings including pharmaceutical cleanrooms including aseptic filling lines, ambulances, and densely populated areas.
Learn more about our Indoor Air Quality applications here
 UV222™
UV222™ UV222 Linear
UV222 Linear UV222 Downlight
UV222 Downlight Vertex 222
Vertex 222.png) UV222 Pendant
UV222 Pendant.png) UV222 Booth
UV222 Booth.png) UV222 Step-On
UV222 Step-On.png) UV222 Cleanroom Downlight
UV222 Cleanroom Downlight UV222 Dual Downlight 60x60
UV222 Dual Downlight 60x60 UV222 Material Airlock
UV222 Material Airlock UV222 Ambulance
UV222 Ambulance UV222 Compact
UV222 Compact UV222 Industrial
UV222 Industrial

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)